Contents
Introduction
Overview of Solar Battery Banks
Hey there! If you’re curious about solar battery banks, you’ve come to the right place. Let’s break it down: a solar battery bank is a system that stores energy generated by your solar panels so you can use it whenever you need. Think of it as a giant rechargeable battery for your house.
Why should you care about this? Well, solar battery banks offer some pretty awesome benefits. First off, they give you energy independence. If the power goes out, you’re covered. No more being at the mercy of power outages! Plus, they help you save money in the long run by reducing your reliance on the grid. Not to mention, using solar energy is fantastic for the environment. You’re cutting down on fossil fuels and reducing your carbon footprint. Win-win, right?
Importance in Renewable Energy Systems
Solar battery banks play a crucial role in modern renewable energy systems. Whether you’re looking to go completely off-grid, or you just want to supplement your existing power supply, a solar battery bank can be a game-changer. It stores all that precious solar energy your panels collect during the day, so you can use it at night or on cloudy days when the sun isn’t shining.
Let’s talk benefits. By using a solar battery bank, you’re not just saving money; you’re also helping the planet. Reducing reliance on traditional power sources means fewer greenhouse gas emissions. Plus, it’s a great way to ensure you have power when you need it most. Imagine having a backup during a storm or a power outage. You’ll have peace of mind knowing your home can stay powered up regardless of what’s happening with the local grid.
In short, a solar battery bank is a smart, sustainable investment that pays off in more ways than one. So, let’s dive into how you can build your very own solar battery bank!
Planning and Preparation
Assessing Energy Needs
Alright, let’s get started with planning your solar battery bank. The first step is figuring out how much energy you actually use. This might sound a bit technical, but don’t worry—it’s pretty straightforward.
Think about everything in your home that uses electricity: lights, appliances, gadgets, and so on. You need to calculate your daily energy consumption. An easy way to do this is by looking at your electricity bill. It usually shows how many kilowatt-hours (kWh) you use per month. Just divide that number by 30 to get your daily usage.
Once you know your daily energy needs, you can estimate how much power your solar panels will generate. This depends on factors like the size of your panels, the amount of sunlight your area gets, and the efficiency of the panels. There are plenty of online calculators that can help you with this part.
Choosing the Right Location
Next up is picking the perfect spot for your solar battery bank. Location is key here. You’ll want to decide whether to place it indoors or outdoors. Indoor placements are great for protecting your batteries from the elements, but they require good ventilation to prevent overheating. On the other hand, outdoor placements need weatherproofing but can save indoor space.
Consider the environmental factors too. Extreme temperatures and humidity can affect battery performance. Make sure your chosen spot is dry, cool, and well-ventilated.
Budgeting and Costs
Now, let’s talk money. Building a solar battery bank is an investment, but it’s one that pays off over time. You need to budget for the initial setup costs, which include buying the batteries, solar panels, charge controllers, inverters, and other necessary components.
It’s also smart to compare different battery types and brands. Some might be cheaper upfront but have a shorter lifespan, while others might cost more initially but last longer and perform better. Don’t forget to factor in potential savings on your electricity bills over time, which can make the initial investment worth it.
By taking these steps—assessing your energy needs, choosing the right location, and budgeting—you’ll be well-prepared to build an efficient and effective solar battery bank. Next, we’ll dive into understanding the different types of batteries you can use. Stay tuned!
Understanding Battery Types

Lead-Acid Batteries
Alright, let’s talk batteries. First up, lead-acid batteries. These are the old-school, tried-and-true option. They’ve been around for ages and are pretty reliable. They’re also generally cheaper than other types, which makes them a popular choice for those just getting started with solar battery banks.
However, they do have some downsides. Lead-acid batteries are heavy and bulky, and they don’t last as long as some newer technologies. They also require regular maintenance, like checking the water levels and cleaning the terminals. If you’re okay with a bit of upkeep and want to keep costs low, lead-acid batteries might be a good fit for you.
Lithium-Ion Batteries
Next up, we have lithium-ion batteries. These are the high-tech, modern option. You probably have lithium-ion batteries in your phone or laptop. They’re lightweight, compact, and have a long lifespan. Plus, they require very little maintenance, which is a big plus.
The downside? They’re more expensive upfront. But, considering their long life and high efficiency, many people find that the extra cost is worth it. If you’re looking for a set-it-and-forget-it solution and don’t mind spending a bit more, lithium-ion batteries are a great choice.
Nickel-Cadmium and Nickel-Metal Hydride Batteries
Lastly, we have nickel-cadmium (NiCd) and nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries. These aren’t as common for home solar battery banks, but they’re still worth mentioning. NiCd batteries are tough and can handle extreme temperatures, but they’re also toxic and not very eco-friendly. NiMH batteries are more environmentally friendly and have a good lifespan, but they’re more expensive than lead-acid and less efficient than lithium-ion.
So, why consider these? If you’re in a situation where temperature extremes are a concern, NiCd might be worth a look. If you want something eco-friendlier and don’t mind the extra cost, NiMH could be a good middle ground.
Conclusion
In summary, choosing the right battery type depends on your needs and budget. Lead-acid batteries are affordable and reliable but require maintenance. Lithium-ion batteries are efficient and low-maintenance but come with a higher upfront cost. Nickel-based batteries offer unique benefits for specific situations. Understanding these options will help you make an informed decision as you build your solar battery bank. Up next, we’ll cover the essential components you’ll need. Stay tuned!
Components of a Solar Battery Bank

Solar Panels
Let’s start with the star of the show: solar panels. These are the devices that capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. There are three main types of solar panels you’ll come across: monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film.
- Monocrystalline panels are the most efficient and long-lasting, but they’re also the most expensive. They’re made from a single crystal structure, which makes them more efficient at converting sunlight into electricity.
- Polycrystalline panels are a bit less efficient but also cheaper. They’re made from multiple crystal structures, which makes them less efficient but more affordable.
- Thin-film panels are the least efficient but the cheapest and most flexible. They’re great if you have a lot of space and need a lower-cost option.
When choosing your solar panels, consider the size of your roof or the area where you’ll install them, your budget, and your energy needs.
Charge Controllers
Next up is the charge controller. This little device is crucial because it regulates the power coming from your solar panels to your batteries. Without it, your batteries could get overcharged, which can damage them.
There are two main types of charge controllers: PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) and MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking).
- PWM controllers are simpler and cheaper, but they’re not as efficient as MPPT controllers.
- MPPT controllers are more expensive but much more efficient, especially in low-light conditions. They can extract the maximum possible power from your solar panels.
If you can afford it, go for an MPPT controller. It’ll make your system more efficient and extend the life of your batteries.
Inverters
Inverters are another essential component. They convert the DC (direct current) electricity from your solar panels and batteries into AC (alternating current) electricity, which is what most home appliances use.
There are two main types of inverters: pure sine wave and modified sine wave.
- Pure sine wave inverters produce a smooth, consistent wave of electricity, just like the power from the grid. They’re ideal for sensitive electronics and are generally more efficient.
- Modified sine wave inverters are cheaper but produce a rougher wave, which can cause issues with some electronics and appliances.
For the best performance and to protect your devices, it’s worth investing in a pure sine wave inverter.
Battery Management System (BMS)
Finally, let’s talk about the Battery Management System (BMS). This is a critical part of your solar battery bank because it monitors and manages the state of your batteries.
The BMS ensures that each battery cell is charged and discharged evenly, which helps to prolong the lifespan of your batteries and improve safety. It also protects against issues like overcharging, overheating, and short circuits.
In summary, building a solar battery bank involves several key components: solar panels to capture sunlight, charge controllers to regulate power, inverters to convert electricity, and a BMS to manage your batteries. Understanding these components will help you create a reliable and efficient system. Next, we’ll dive into designing your battery bank. Stay tuned!
Designing the Battery Bank
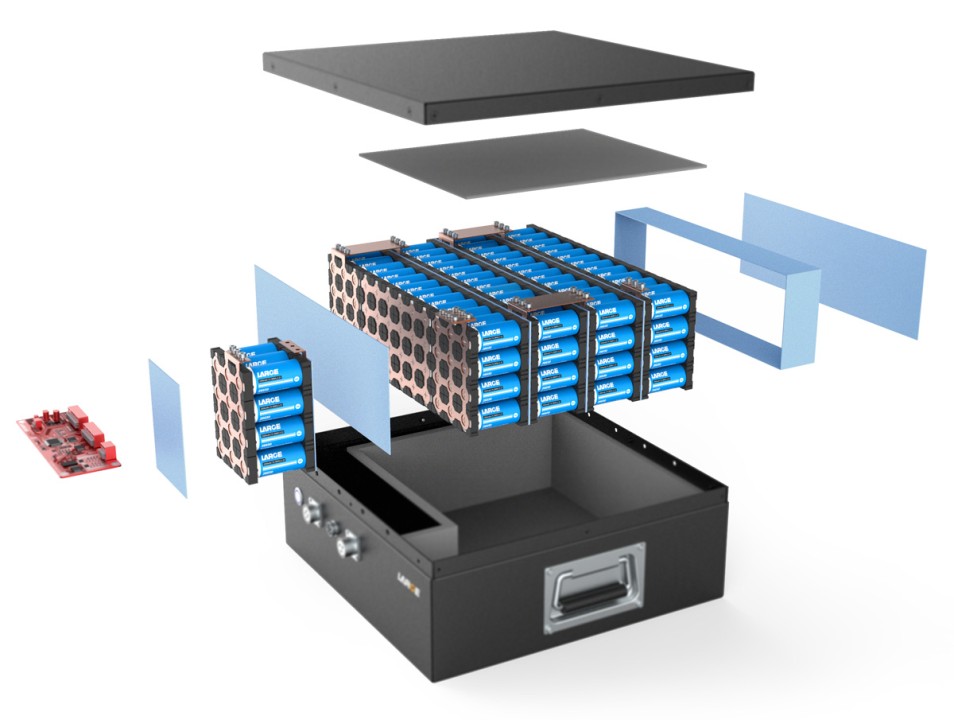
Sizing the Battery Bank
Alright, let’s get into the nuts and bolts of designing your solar battery bank. First things first: sizing your battery bank. This step is crucial because you want to make sure your batteries can store enough energy to meet your needs without breaking the bank.
To start, you need to think about the depth of discharge (DoD). This is how much of the battery’s capacity you can use without damaging it. Most batteries have a recommended DoD to maintain a long lifespan. For example, if a battery has a 50% DoD, you can only use half of its total capacity before it needs to be recharged.
Next, calculate the total capacity you need. This is typically measured in amp-hours (Ah) or kilowatt-hours (kWh). Use your daily energy consumption (remember, we figured that out in the planning stage) and factor in a bit of extra capacity to cover cloudy days or higher-than-usual usage.
Wiring and Configuration
Now that you know how big your battery bank needs to be, it’s time to think about wiring and configuration. This part might sound a bit technical, but don’t worry—we’ll keep it simple.
There are two main ways to connect batteries: series and parallel.
- Series connections increase the voltage but keep the capacity (Ah) the same. This is useful if you need a higher voltage system.
- Parallel connections increase the capacity but keep the voltage the same. This is useful if you need more storage capacity without changing the voltage.
Most systems use a combination of both series and parallel connections to get the desired voltage and capacity. Just make sure you use the right gauge of wire and proper connectors to ensure safety and efficiency.
Choosing Additional Components
Beyond the batteries and wiring, you’ll need a few more components to complete your system. These include fuses, breakers, and disconnects.
- Fuses and breakers protect your system from overloads and short circuits. Think of them as safety valves that prevent damage to your expensive equipment.
- Disconnects allow you to safely disconnect parts of your system for maintenance or emergencies. These are especially important for isolating your batteries from the rest of the system when needed.
Finally, consider investing in a monitoring system or software. These tools let you keep an eye on your battery bank’s performance, so you can spot issues early and make adjustments to improve efficiency.
Conclusion
Designing your solar battery bank involves careful planning and a good understanding of how different components work together. By sizing your battery bank correctly, wiring it properly, and choosing the right additional components, you’ll create a reliable and efficient system. Next, we’ll walk through the installation process step-by-step. Stay tuned!
Installation Process
Safety Precautions
Before diving into the installation, let’s talk safety. Working with electricity can be dangerous, so taking the right precautions is essential. Always wear personal protective equipment (PPE) like gloves and safety glasses. Make sure your work area is dry and free of clutter to avoid any accidents.
Handling batteries and electrical components requires care. Batteries can be heavy and contain hazardous materials, so use proper lifting techniques and handle them gently to prevent leaks or damage. When dealing with wiring, make sure all power sources are disconnected to avoid electric shocks.
Setting Up the Battery Bank
Now that we’ve covered safety, let’s set up your battery bank. Here’s a step-by-step guide to get you started:
- Prepare the Battery Bank Area: Choose a dry, well-ventilated area. Set up any racks or shelves to hold your batteries securely.
- Place the Batteries: Position your batteries on the racks or shelves. Make sure they’re stable and there’s enough space around them for ventilation.
- Connect the Batteries: Depending on your design, connect the batteries in series, parallel, or a combination of both. Use the correct gauge of wire and secure all connections tightly.
- Install the Battery Management System (BMS): Connect the BMS to your batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions. This will help monitor and manage your battery health.
Common Pitfalls and Troubleshooting Tips
Even with careful planning, issues can arise during installation. Here are some common pitfalls and how to avoid them:
- Loose Connections: Always double-check your connections. Loose wires can lead to poor performance or even dangerous sparks.
- Improper Sizing: Ensure your wires and components are correctly sized for your system. Using undersized wires can cause overheating.
- Overlooking Ventilation: Batteries need good airflow to stay cool. Ensure your battery bank has adequate ventilation to prevent overheating.
If you run into problems, consult your components’ manuals or seek advice from online forums and communities. Don’t hesitate to ask for professional help if needed.
Connecting the Solar Panels
With your battery bank set up, it’s time to connect the solar panels. Follow these steps:
- Mount the Panels: Install your solar panels on the roof or another sunny location. Ensure they’re securely mounted and positioned to get maximum sunlight.
- Wire the Panels: Connect the solar panels to each other, then run the wires to your charge controller. Follow the wiring diagram provided by the panel manufacturer.
- Connect to the Charge Controller: Attach the solar panel wires to the charge controller, ensuring the correct polarity. The charge controller will regulate the power going to your batteries.
Testing and Verifying Connections
After everything is connected, it’s crucial to test your system. Turn on your charge controller and inverter, and check that everything is working correctly. Use a multimeter to verify that the voltage and current are as expected. Make sure your monitoring system is providing accurate data and that there are no error messages.
Integrating with the Home Power System
Finally, let’s integrate your solar battery bank with your home power system. You have two main options: grid-tied or off-grid.
- Grid-Tied Systems: Connect your inverter to your home’s electrical panel. This allows you to use solar power when available and draw from the grid when necessary. You can even sell excess power back to the grid in some areas.
- Off-Grid Systems: Your inverter will supply power directly to your home’s circuits. Make sure you have a backup generator or other power source for times when solar power isn’t sufficient.
Conclusion
Installing a solar battery bank involves careful attention to safety, detailed setup steps, and thorough testing. By following these guidelines, you’ll ensure your system is safe, efficient, and reliable. Next, we’ll look at how to maintain and monitor your solar battery bank to keep it running smoothly. Stay tuned!
Maintenance and Monitoring
Regular Maintenance Tasks
Keeping your solar battery bank in top shape requires some regular maintenance. Don’t worry, it’s not too complicated. Here are the main tasks you’ll need to stay on top of:
- Cleaning: Dust and dirt can accumulate on your solar panels, reducing their efficiency. Clean them periodically with a soft cloth and soapy water. Avoid harsh chemicals that could damage the panels.
- Inspecting Components: Regularly check your batteries, wiring, and connections for any signs of wear or damage. Look for corrosion on battery terminals and loose wires. Catching issues early can prevent bigger problems down the line.
- Checking and Balancing Batteries: For lead-acid batteries, check the water levels and top them up with distilled water if necessary. For lithium-ion batteries, make sure the Battery Management System (BMS) is balancing the cells correctly.
Monitoring System Performance
To get the most out of your solar battery bank, it’s important to keep an eye on its performance. Thankfully, modern technology makes this easier than ever. Here’s how you can monitor your system:
- Using Monitoring Tools and Apps: Many solar systems come with monitoring tools or apps that provide real-time data on your energy production and consumption. These tools can alert you to any issues and help you optimize your system’s performance.
- Analyzing Data for Efficiency Improvements: Look at your monitoring data regularly to see how well your system is performing. Are there times when you’re producing more energy than you’re using? Or times when you’re running low? Use this information to adjust your energy usage or consider expanding your system.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with regular maintenance and monitoring, issues can arise. Here are some common problems and how to troubleshoot them:
- Performance Drops: If your system isn’t producing as much power as it should, check your solar panels for dirt or shading. Make sure all connections are secure and that your charge controller and inverter are functioning properly.
- Battery Failures: If a battery isn’t holding a charge, it might be time to replace it. Check the BMS for any error messages and ensure all cells are balanced. Lead-acid batteries may need to be desulfated.
- Inverter Issues: If your inverter isn’t converting power properly, check the wiring and connections. Make sure it’s not overheating and that it’s compatible with your battery bank’s voltage.
Conclusion
Maintaining and monitoring your solar battery bank ensures it runs efficiently and lasts as long as possible. By staying on top of regular maintenance tasks, using monitoring tools, and troubleshooting issues promptly, you’ll keep your system in great shape. Up next, we’ll dive into some advanced topics, like expanding your battery bank and smart energy management. Stay tuned!
Advanced Topics
Expanding Your Battery Bank
As you get more comfortable with your solar battery bank, you might want to expand it to increase your energy storage capacity. Here’s how to go about it:
- Assessing Additional Energy Needs: Before expanding, calculate how much more energy you need. Look at your current energy usage and consider any future increases, like new appliances or changes in your lifestyle.
- Selecting Compatible Batteries: When adding new batteries, make sure they’re compatible with your existing ones. Mixing different types or capacities of batteries can lead to inefficiencies and reduce the overall lifespan of your system. It’s best to use the same brand and model.
- Connecting Additional Batteries: Connect the new batteries in series or parallel with your existing ones, depending on your system’s design. Ensure all connections are secure and that the new batteries are integrated into the Battery Management System (BMS).
Integrating with Smart Home Systems
Integrating your solar battery bank with smart home systems can optimize energy usage and enhance convenience. Here’s how you can do it:
- Using Smart Inverters: Smart inverters can communicate with your home’s energy management system to optimize energy usage. They can prioritize solar power during peak sunlight hours and switch to battery power during peak demand times.
- Energy Management Apps: Many smart home systems come with apps that let you monitor and control your energy usage. These apps can show real-time data, predict energy needs, and automate energy-saving tasks.
- Automating Energy Use: Set up your smart home system to automatically adjust energy usage based on your preferences. For example, you can program it to charge your batteries when electricity rates are low or to power specific devices only during peak solar production times.
Utilizing Time-of-Use (TOU) Rates
Time-of-Use (TOU) rates charge different prices for electricity based on the time of day. Here’s how to make the most of them with your solar battery bank:
- Understanding TOU Rates: Know when your electricity rates are highest and lowest. Typically, rates are higher during peak demand hours (like early evening) and lower during off-peak hours (like late night).
- Programming Your System: Program your solar battery system to charge the batteries during off-peak hours when rates are low. Use stored energy during peak hours to avoid high electricity costs.
- Maximizing Savings: By aligning your energy usage with TOU rates, you can maximize savings. Use high-energy appliances (like washing machines or dishwashers) during off-peak hours, and rely on your solar battery bank during peak hours.
Conclusion
Expanding your solar battery bank, integrating it with smart home systems, and utilizing Time-of-Use rates are advanced strategies that can optimize your energy usage and increase savings. These techniques allow you to customize your solar setup to better fit your lifestyle and energy needs. In the final section, we’ll explore the benefits of going off-grid and provide some final tips and resources. Stay tuned!
Future Trends in Solar Battery Technology

Emerging Battery Technologies
The world of solar battery technology is constantly evolving, with researchers and manufacturers exploring new innovations to improve efficiency, lifespan, and sustainability. Here are some emerging battery technologies to keep an eye on:
- Solid-State Batteries: These batteries use solid electrolytes instead of liquid electrolytes found in traditional lithium-ion batteries. They promise higher energy density, longer lifespan, and improved safety.
- Flow Batteries: Flow batteries store energy in liquid electrolytes contained in external tanks. They can be scaled up easily and offer longer cycle life compared to traditional batteries.
- Graphene-Based Batteries: Graphene, a form of carbon, is being researched for its potential to enhance battery performance, including faster charging times and increased capacity.
Innovations in Solar Energy Storage
In addition to advancements in battery technology, there are innovations in how solar energy is stored and managed. Here are a few trends shaping the future of solar energy storage:
- Hybrid Energy Systems: Integrating solar with other renewable sources like wind or hydroelectric power can provide more stable and reliable energy supply.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain is being explored to enable peer-to-peer trading of solar energy between users, enhancing energy independence and efficiency.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms can optimize energy storage and usage by predicting energy demand, adjusting system settings in real-time, and maximizing efficiency.
Sustainable Practices in Battery Manufacturing
As the demand for solar battery systems grows, so does the focus on sustainability in manufacturing practices. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting practices such as:
- Recycling Programs: Developing efficient methods to recycle and reuse battery materials, reducing environmental impact.
- Carbon Footprint Reduction: Using renewable energy sources in manufacturing processes to minimize carbon emissions.
- Ethical Sourcing: Ensuring that raw materials used in batteries are sourced ethically and responsibly, considering social and environmental impacts.
Conclusion
The future of solar battery technology holds exciting possibilities for improving efficiency, sustainability, and affordability. Keeping up with these trends can help you make informed decisions as you build and expand your solar battery bank. As technology continues to advance, the potential for harnessing solar energy for everyday use grows stronger. In the final section, we’ll wrap up with a summary of key points and additional resources for further exploration. Stay tuned!
Conclusion and Additional Resources
Summary of Key Points
Let’s summarize what we’ve covered about building a solar battery bank:
- Introduction to Solar Battery Banks: We explored what solar battery banks are and why they’re beneficial, offering energy independence, cost savings, and environmental benefits.
- Planning and Preparation: We discussed assessing energy needs, choosing the right location, and budgeting for initial setup costs.
- Understanding Battery Types: Detailed information on different types of batteries including lead-acid, lithium-ion, and others, highlighting their pros and cons.
- Components of a Solar Battery Bank: An overview of essential components like solar panels, charge controllers, inverters, and Battery Management Systems (BMS).
- Designing the Battery Bank: Steps to size your battery bank, wire it correctly, and choose additional components like fuses and disconnects.
- Installation Process: Safety precautions, setting up the battery bank, connecting solar panels, and integrating with your home’s power system.
- Maintenance and Monitoring: Regular tasks to keep your system running smoothly, monitoring performance, and troubleshooting common issues.
- Advanced Topics: Expanding your battery bank, integrating with smart home systems, and optimizing energy usage with Time-of-Use rates.
- Future Trends in Solar Battery Technology: Emerging technologies, innovations in energy storage, and sustainable practices in battery manufacturing.
Additional Resources for Further Exploration
To continue your journey into solar battery banks and renewable energy, here are some useful resources:
- Websites and Blogs: Explore websites like Solar Power World, CleanTechnica, and EnergySage for articles, guides, and news updates.
- Books: Consider books like “Solar Electricity Handbook” by Michael Boxwell and “The Battery Technology Handbook” by H.A. Kiehne for in-depth knowledge.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera and edX offer courses on solar energy and renewable technologies.
- Local Workshops and Seminars: Check with local renewable energy organizations or universities for workshops and seminars on solar power.
Conclusion
Building a solar battery bank is not just about harnessing renewable energy—it’s about creating a sustainable future for yourself and the planet. By understanding the technology, planning carefully, and staying informed about advancements, you can create a system that meets your energy needs efficiently and effectively.

Dr. Alexander Tabibi is an entrepreneur, investor, and advocate for sustainable innovation with a deep commitment to leveraging technology for environmental and social good. As a thought leader at the intersection of business and sustainability, Dr. Tabibi brings a strategic vision to Green.org, helping guide its mission to inspire global climate awareness and actionable change.
With a background in both medicine and business, Dr. Tabibi combines analytical rigor with entrepreneurial insight.

